
MOTS-c (Mitochondrial Open Reading Frame of the 12S rRNA-c) is a mitochondrial-derived peptide studied for its potential role in cellular metabolism and energy regulation. Researchers are particularly interested in MOTS-c because it appears to influence metabolic signaling pathways associated with glucose utilization and mitochondrial function.
Below is an SEO-optimized, research-focused overview of MOTS-c benefits explored in scientific literature.
What Is MOTS-c?
MOTS-c is a small peptide encoded by mitochondrial DNA. Unlike most peptides that are encoded in nuclear DNA, MOTS-c originates within the mitochondria, which are responsible for cellular energy production.
It has been investigated in laboratory studies related to:
- Metabolic homeostasis
- Skeletal muscle physiology
- Glucose metabolism
- Cellular stress adaptation
MOTS-c Benefits Studied in Research
1. Metabolic Regulation
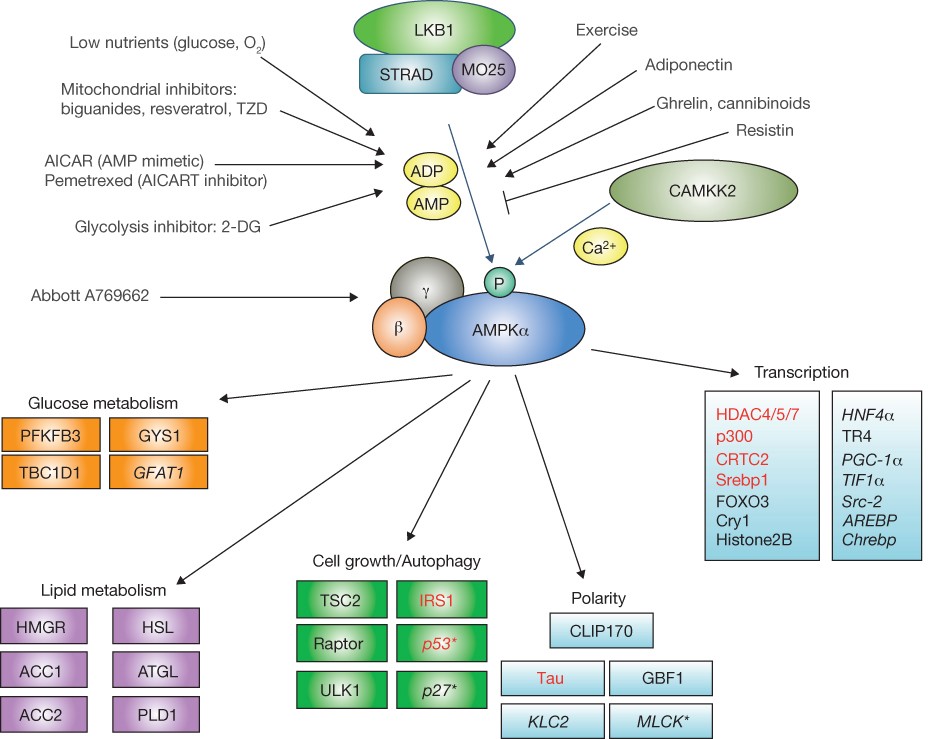
One of the primary areas of MOTS-c research involves its influence on metabolic pathways. Studies suggest MOTS-c may interact with:
- AMPK signaling pathways
- Glucose transport mechanisms
- Lipid metabolism processes
These pathways are central to how cells manage energy resources.
2. Mitochondrial Function Research
Because MOTS-c is mitochondrial-derived, it is closely linked to mitochondrial signaling and function. Researchers examine its potential involvement in:
- Bioenergetic efficiency
- Oxidative stress response
- Cellular adaptation to metabolic stress
This makes MOTS-c relevant in studies focused on energy regulation at the cellular level.
3. Glucose Metabolism Studies
Laboratory models have explored how MOTS-c influences glucose utilization and insulin-related signaling pathways. Research suggests it may affect:
- Glucose uptake in muscle cells
- Insulin sensitivity pathways
- Systemic metabolic regulation models
These findings are still under investigation and remain within research settings.
4. Exercise and Muscle Research
MOTS-c has been examined in experimental models related to skeletal muscle physiology and exercise adaptation. Researchers study whether it plays a role in:
- Muscle metabolic flexibility
- Endurance-related cellular signaling
- Adaptation to metabolic stress
This has generated interest in sports science and metabolic research communities.
5. Longevity and Aging Research
Because mitochondrial health is often studied in relation to aging biology, MOTS-c has become a topic of interest in longevity research models. Investigators evaluate:
- Age-related mitochondrial signaling changes
- Cellular resilience pathways
- Metabolic efficiency markers
Ongoing studies aim to better understand these relationships.
Why MOTS-c Is a Focus in Research
MOTS-c stands out because it represents:
- A mitochondrial-encoded peptide
- A potential regulator of cellular energy balance
- A link between mitochondrial signaling and systemic metabolism
As a result, it continues to be examined in metabolic and cellular biology research environments.
Conclusion
MOTS-c benefits explored in research primarily involve metabolic regulation, mitochondrial signaling, glucose metabolism, and skeletal muscle physiology. While promising findings have emerged in laboratory studies, MOTS-c remains an investigational peptide studied in controlled research settings.
⚠ Strict Research Use Only (RUO) Disclaimer
All peptides and research compounds sold by HealthLab Peptides are strictly Research Use Only (RUO). They are not for human or veterinary use, not intended for diagnosis, treatment, cure, or prevention of any disease, and must be handled only by qualified research professionals in controlled laboratory environments.




 BPC-157 and TB-500 10mg WOLVERINE STACK
BPC-157 and TB-500 10mg WOLVERINE STACK  GHRP-2 5mg
GHRP-2 5mg  GLP-1 Sema 20mg
GLP-1 Sema 20mg  Tesamorelin 10mg
Tesamorelin 10mg